By Eliot Higgins from Bellingcat, for The First Draft
As verification and open source investigation techniques and methodologies have developed over the last few years, so have the various tools and platforms used to access the information that makes this kind of work possible. In this article, we examine some of these tools, and the different uses they have in the verification and investigation process.
Googling Earth
For many investigations, Google Earth has become an essential tool for verifying images and videos and plays a key role in the process of geolocation. Geolocation is a verification method where the landmarks and features visible in photographs or videos can be compared against other images to help confirm where they were captured. At its most basic, Google Earth allows access to satellite imagery from across the globe but it also has a number of other features that play a useful role in verification.
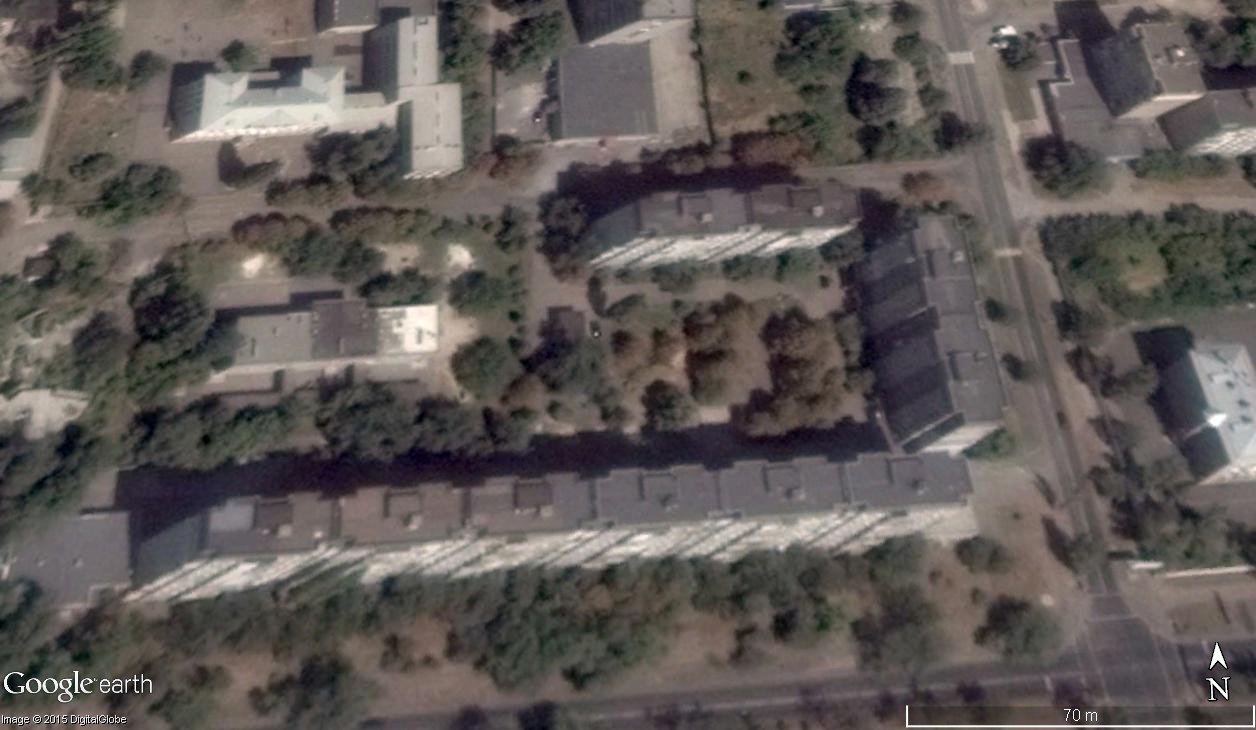
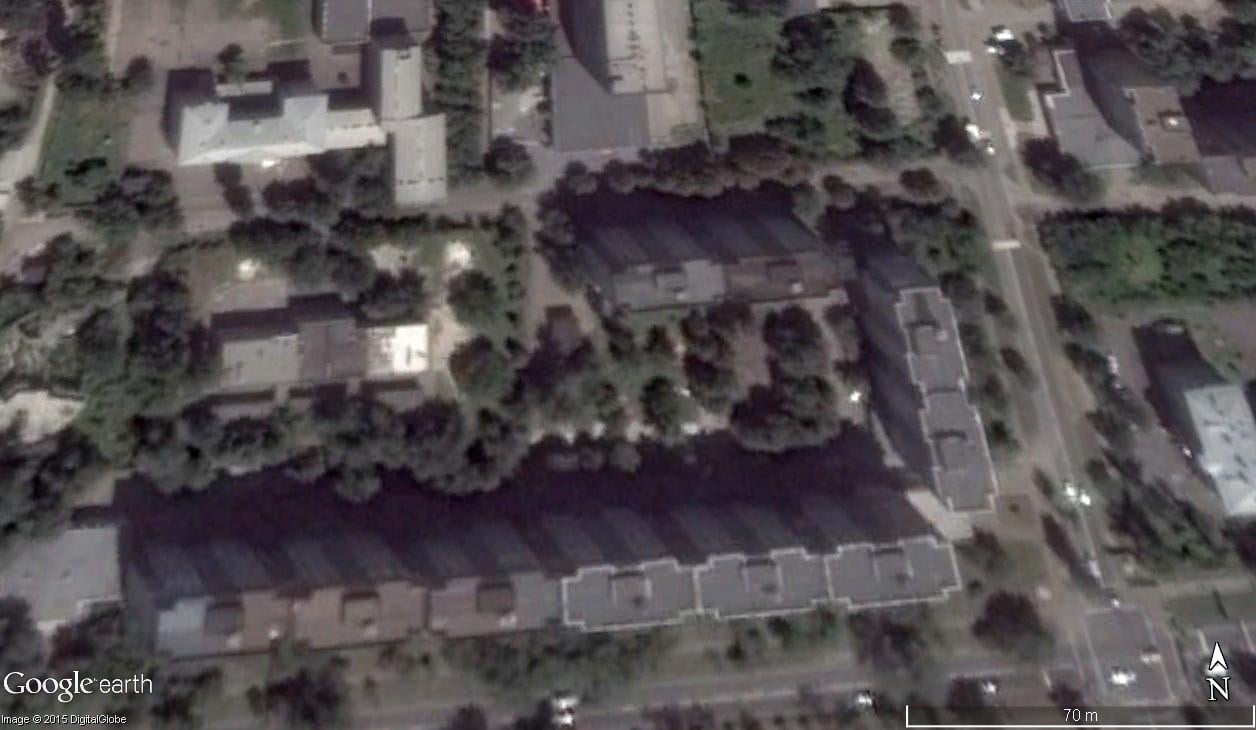
One feature that is often overlooked is historical imagery, which can be easily found under the “view” menu. When switched on, the user is presented with a slider that allows them to change the displayed image to any historical image available on Google Earth. This is useful for a number of reasons; for example, the position of the satellite when it records an image might give you a view of one side of a building, but other images taken at different times might give you a different view. The example below shows the same location on two different dates, providing a view of two different sides of the buildings.


Another useful feature is the “Photos” layer, which displays photos from a number of sources, most importantly Panoramio. Panoramio is a website where users can upload geotagged photos, and those photos are then visible on Google Earth. This layer helps you to explore ground level images from locations that you might be need to examine in more detail.
Comparing historical images can help you to match the features of a building in a photograph or video.
The View from the Street
Ground level images are hugely useful for geolocation and can be accessed through street view features on Google Maps and Google Earth, which many people are familiar with. The Russian website Yandex Maps is less well known, but much of their collection of street view imagery is of locations not yet available on Google Street View.
Having an awareness of these different tools is important because you can compare information based on the details that you have available. It is necessary to consider the date that street view images were recorded, for example. In this recent piece, verifying where a MH17 related video was recorded, Yandex Maps imagery showed the location in question but the billboards visible in the video were absent. However, Google Earth satellite imagery showed that the billboards were a recent addition to the area and the Yandex Maps imagery was recorded before the billboards were constructed.
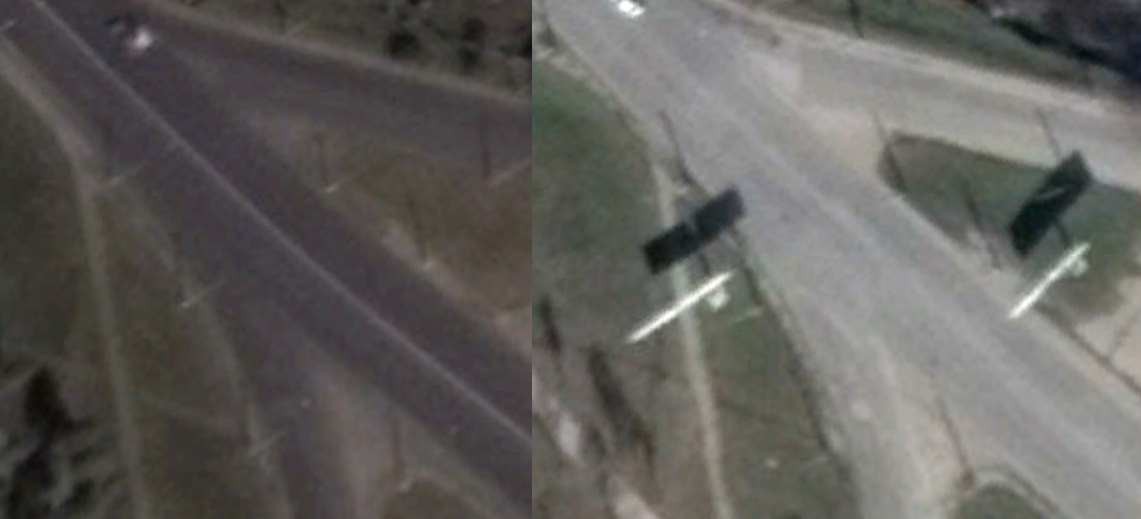

By comparing images from Yandex Maps with other information about the area (for example, a recently constructed church), it was possible to verify the date of the Yandex Maps imagery. This demonstrates another overlooked facet of geolocation and verification, you not only need to verify the image that you’re investigating, but also any reference images. Something like a geotag can be inaccurate or changed, so it must be verified as part of a robust process.
A World of Geotags
Recently, new platforms have been developed that make geotags even more useful as part of the verification process. Yomapic is a free website that allows geographical searches of geotagged images posted to the popular Russian social media site VKontakte and Instagram. In the below example, Yomapic displays images posted from the Islamic State controlled town of Raqqa in the last week.
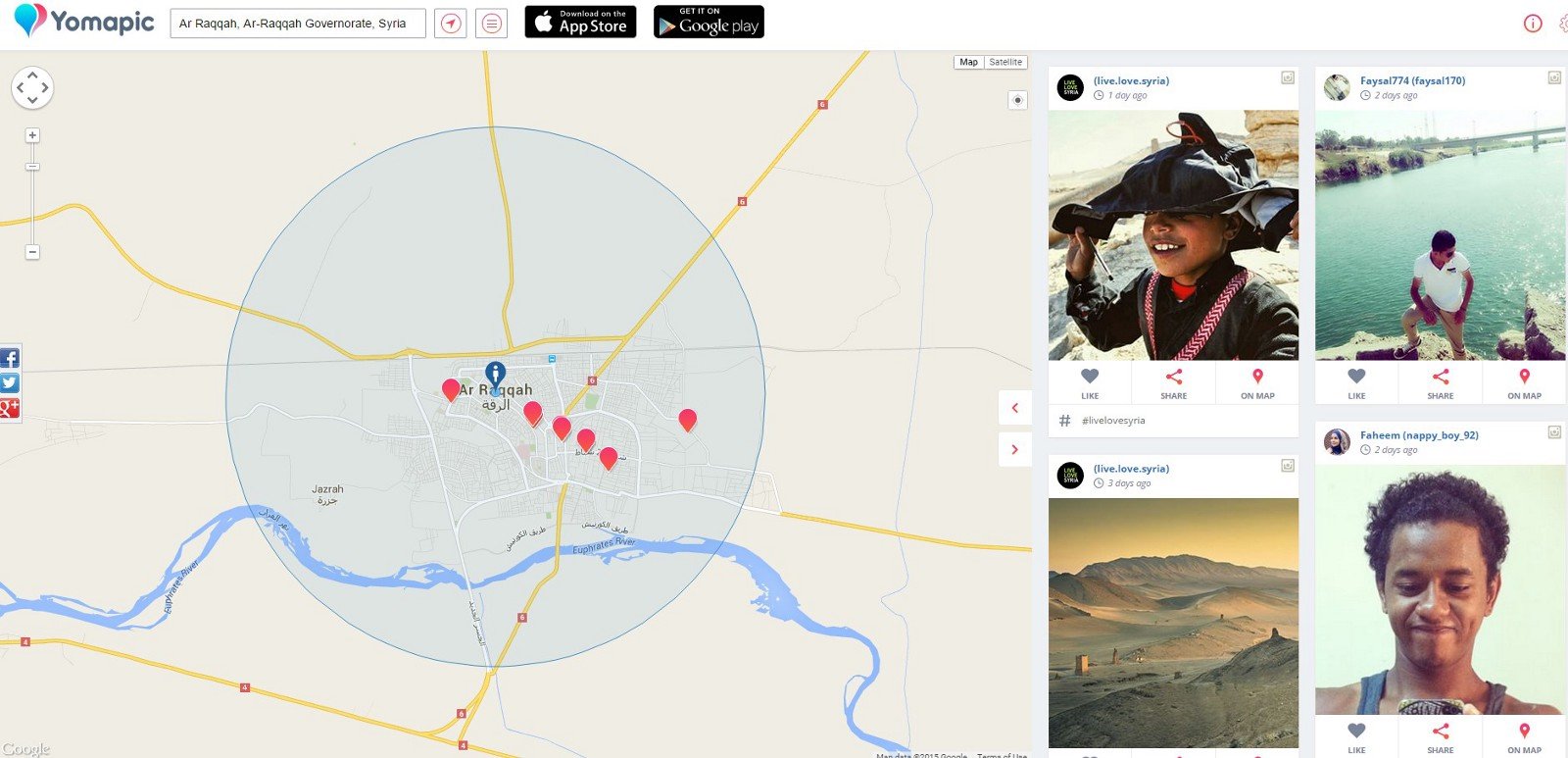
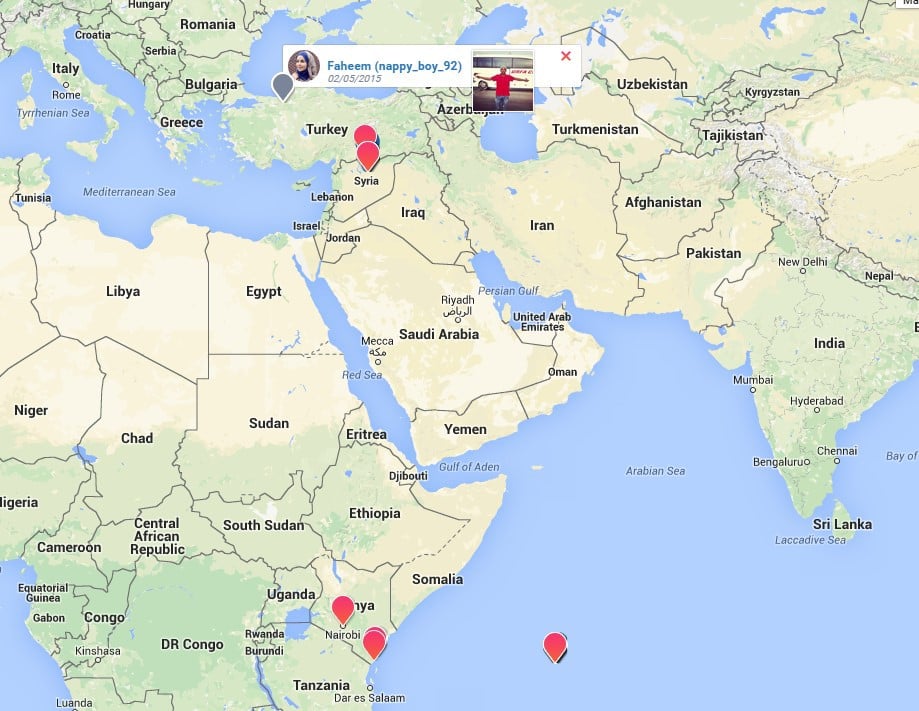
An interesting feature of Yomapic is it’s possible to select an individual account by clicking on the username, displaying all images on the account, geotagged or not. The below image shows on Instagram user as they travel from the Seychelles to Kenya, then on to Turkey and finally Raqqa, Syria.
An alternative to Yomapic is EchoSec, which includes many more social media sites in its searches, including Twitter, Facebook, YouTube, Panoramio, and Flickr. It also has a date range search, which is extremely useful when investigating past events.
While the obvious use for Yomapic and EchoSec is to discover posts related to specific events in an area, it’s also valuable in another way. When geolocating images it might not be possible to find street view imagery or Panoramio photographs, but thanks to Yomapic and EchoSec, it’s possible to see if anyone in the local area may have posted an Instagram photo or YouTube video revealing visual clues about the location that you’re interested in. This adds to the range of options you have when searching for reference images and combining these tools makes efforts to verify content far more effective.
Bellingcat is a member of First Draft, a coalition of experts sharing top tips and training in how to handle eyewitness media.
Published by Medium.com.





